From Fragile to Resilient: Reengineering the Cardiac Device Clinic Lifecycle
Cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED) monitoring is one of healthcare’s largest and longest-standing telehealth service lines. What began as periodic pacemaker checks has evolved into continuous, high-acuity monitoring of increasingly complex cardiac devices. Today, device clinics generate and manage enormous volumes of clinical data that directly influence patient outcomes, clinician decision-making, and cardiovascular service line revenue.
Yet despite its strategic importance, cardiac device monitoring has historically lacked the governance, lifecycle management, and executive visibility applied to other cardiovascular programs. The result is a system that functions—but often under chronic operational strain.
When Instability Becomes Normal
Staffing shortages, workflow fragmentation, growing backlogs, and inconsistent reporting are common across device clinics. Too often, these challenges are treated as inevitable rather than as signals of systemic design risk.
This normalization of instability carries real consequences. Burnout is widespread across cardiology roles, and workload has been identified as one of its strongest predictors. Workforce strain fuels turnover, disrupts continuity of care, and creates revenue leakage through delayed review, billing backlogs, and lost capacity.
The issue is not simply filling vacancies or adopting new tools. As management theorist Peter Drucker noted, some challenges reflect structural discontinuity and require transformation- not incremental fixes.
The Reactive Trap
Most cardiac device clinics operate reactively. Vacancies trigger overtime or redistribution of work. Backlogs prompt short-term fixes. New technology is layered onto existing workflows without clear ownership or governance.
While these responses keep clinics afloat, they limit scalability, predictability, and resilience. By focusing on today’s problems, leaders miss the opportunity to redesign the full operational life cycle- staffing, training, workflows, and technology- as an integrated system.
The Real Problem: A Broken Lifecycle
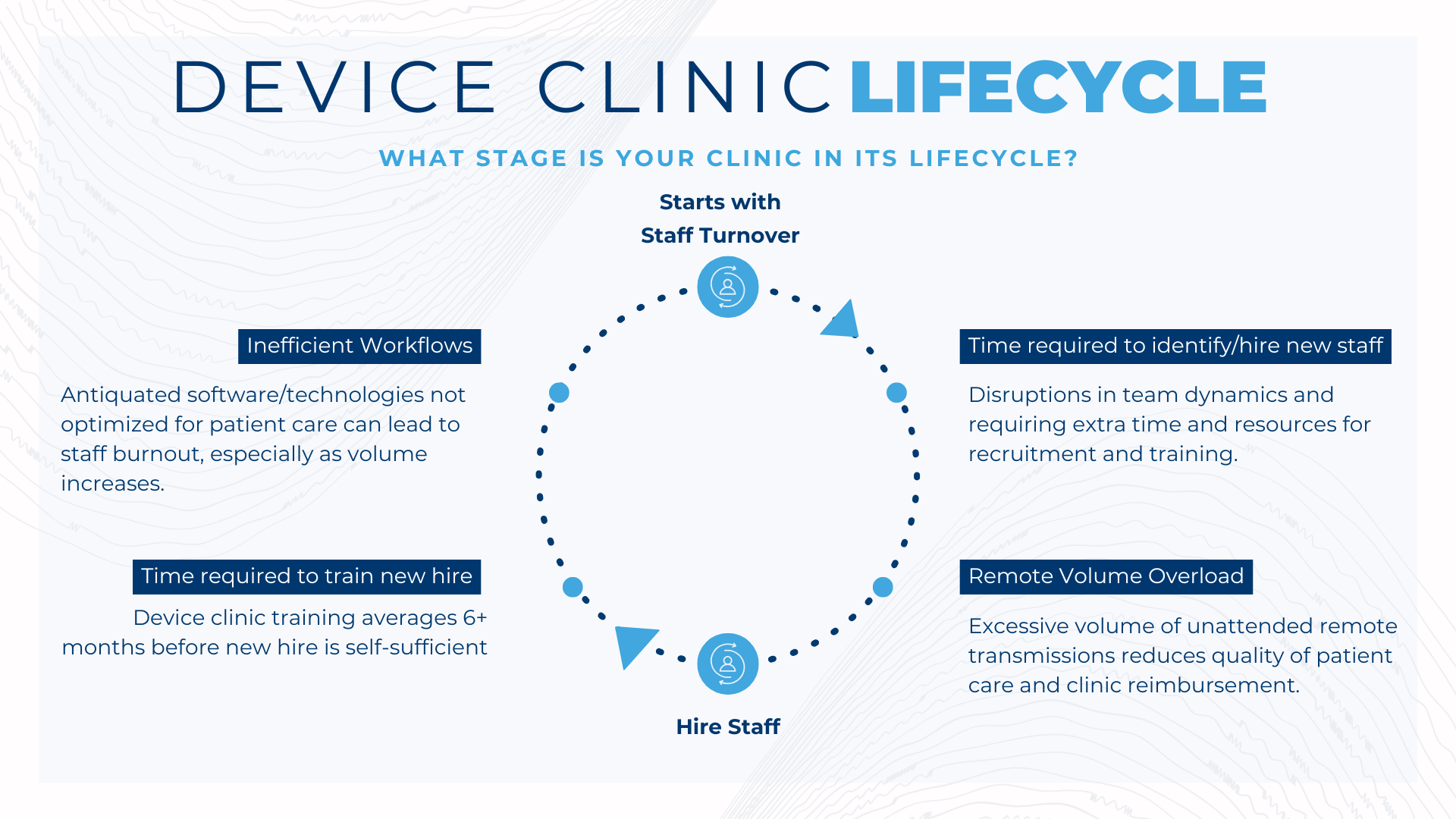
Many device clinics operate within a recurring attrition loop. Staff leave, replacements are difficult to source, backlogs accumulate, and remaining team members absorb the load- until burnout drives the next departure.
Because this dysfunction is absorbed at the operational level, executive oversight is often limited. Fragmented reporting and diffuse ownership obscure the cumulative impact on clinical quality, workforce stability, and financial performance.
At the same time, remote monitoring technology has increased operational complexity. Clinics manage data across multiple proprietary portals, often requiring manual reconciliation and offering little visibility into cumulative workload. Technology alone cannot stabilize a broken lifecycle.
Reengineering the Service Line
Sustainable improvement requires more than patching gaps. It requires operational lifecycle reengineering.
Drawing from Agile management principles increasingly applied in healthcare, lifecycle reengineering emphasizes value-driven delivery, multidisciplinary collaboration, transparent metrics, and continuous adaptation. Applied at the cardiac device service line level, this approach shifts leadership focus from isolated fixes to system design.
The critical question becomes:
What operational model prevents instability from recurring?
Staffing as Infrastructure
Staffing instability is among the most visible and costly elements of lifecycle failure. Recruitment, onboarding, productivity loss, and turnover create significant financial and operational drag—especially in specialized cardiac roles.
Burnout is tightly linked to workload design, not just headcount. This has driven growing recognition of hybrid staffing models that combine in-clinic teams with remote or supplemental support. When aligned with standardized workflows and clinical governance, these models stabilize workload variability, preserve continuity of care, and protect service line throughput during workforce transitions.
PrepMD was built around this reality- providing scalable staffing support that integrates into existing device clinic operations. Rather than functioning as a takeover, PrepMD partners with the clinic team to assess operational needs, identify pressure points, and design customized support models that align with the clinic’s goals, culture, and governance structure.
Training as Retention and Bench-Building
Training remains one of the most underutilized levers for stability and retention. Structured, tiered education strengthens competence, confidence, and job satisfaction while preserving institutional knowledge that is difficult to replace after turnover.
Embedding education into the operational lifecycle – through accredited learning, mentorship, and formal succession planning- creates a ready bench of cross-trained professionals. Clinics that invest in continuous development reduce downtime, mitigate burnout cascades, and maintain performance during transitions.
PrepMD’s education-first model reflects this philosophy: training is not an add-on, but core infrastructure for service line resilience – delivered in collaboration with clinic leadership to strengthen internal capability rather than replace it.
Technology That Connects the Lifecycle
Remote monitoring technology has expanded access to care but often remains siloed, focused on data aggregation rather than operational integration. Without alignment to staffing models, training pathways, and governance frameworks, software alone cannot stabilize a service line.
A sustainable model treats technology as connective tissue – linking people, processes, and performance metrics into a unified operational framework. When designed for lifecycle alignment, technology enables transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement rather than adding friction.
From Reactive to Resilient
Cardiac device monitoring is essential to modern cardiovascular care, yet it has long operated without the lifecycle discipline applied elsewhere in healthcare. The result has been persistent instability, workforce strain, and financial leakage.
Breaking this cycle requires leaders to move beyond isolated fixes and adopt a lifecycle perspective- integrating staffing, training, technology, and governance into a cohesive system. When aligned, CIED monitoring can evolve from reactive to resilient, supporting both patient outcomes and service line performance.
At PrepMD, this lifecycle-based approach is grounded in partnership. We work alongside clinic teams to evaluate operational realities, co-design customized solutions, and strengthen the systems already in place- building resilience together rather than replacing what works.